Nowadays, many talks are spreading around Quantitative Easing, also known as QE, in the financial markets. This topic is the crucial one these days since it can bring unexpected changes of trends and drops of currency prices. The basics of this term are based on increase of the money supply in times, when it is not required by the economy in order to stimulate it.
Although many people are not familiar with the term “Quantitative Easing”, central banks use it as a monetary policy tool when they do not have room to cut interest rates. In 2001, the Bank of Japan coined the term just after taking interest rates to zero. Since they did not have more room to cut rates, they took Quantitative Easing as their second plan.
Quantitative Easing Explained
Quantitative Easing consist of printing money in order to buy a diversity of securities, with the purpose of generating a great quantity of cash or liquidity in the financial markets. After doing this, you will find out that it increases the number of currency in circulation; this situation cuts down the value of the currency and increases inflation overtime.
Imagine that there are only 100 football cards signed by Vince Lombardi, they are worth $2000 each and, suddenly, another 100 Vince Lombardi-signed football cards appear. In this case, you would expect each of them to have a lower price. The moment there are more football cards in the market at lower costs, you will find that there is more activity in the football card market as well. In the case of Quantitative Easing, you will have the same situation.
Once the market is flooding with liquidity, the main target of the central bank will be promoting lending. Of course QE is more complex than football cards, but the principle is highly applicable.
Quantitative Easing Outcome
Since Quantitative Easing was only put in practice once in Japan, there is no specific criterion in this area. However, you have to keep in mind that the outcome of Japan’s zero interest rate policy was analyzed way before bringing US interest rates to a very close margin of Japan’s 2000 levels.
According to some experts, since 2001 until 2006, the Bank of Japan implemented this innovative concept in monetary economics with the purpose of facing a difficult period of economic stagnation and recession. Since the central bank got rates at 0%, it had to start a policy to help the country to stop deflation. At this point, it is vital to understand that deflation is a decline in prices over an extended period of time.
One of the effects of deflation is that consumers stop buying and sellers have to reduce prices. Because of this, the deflation phenomenon could be considered as destructive as the inflation one. On the other hand, all the efforts of Japan lead the BoJ to achieve their easing targets throughout the expansion of the types of securities that they would get.
For example: buying long term treasuries, asset backed securities, equities, and new levels of commercial paper. This process is aimed to flood the financial system with reserves and liquidity to such an extent that it would be necessary to re-establish a normal lending situation.
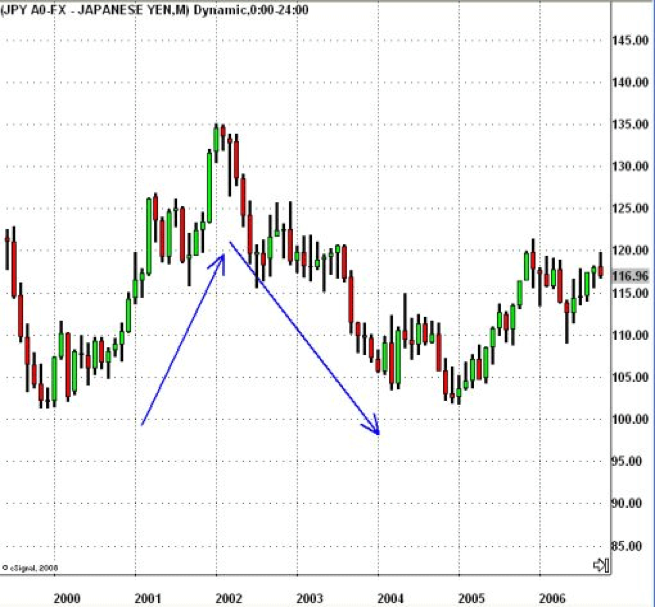
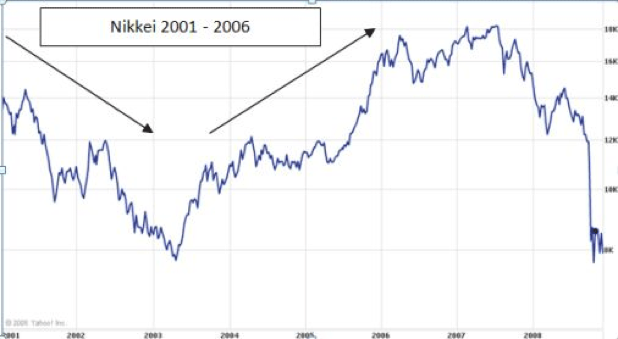
Some statistics reflect that USD/JPY increased 19% during the first years of Quantitative Easing. In this case, a typical reaction to Quantitative Easing is the strengthening of US dollar and the weakening of the Japanese Yen. In addition to that, the Nikkei dropped 28%. While the Japanese economy was stabilizing, the USD/JPY dropped 22% during 2002 and 2004.
However, the Nikkei recovered 20% during the same period mentioned before, but only after falling another 20%. Most people agree that Quantitative Easing stops deflation, but there is still a strong debate about whether this method will be the change in economy or not.
USD/JPY
Nikkei
Federal Reserve Version of Quantitative Easing
There has been a heavy debate about the new version of Quantitative Easing made by the Federal Reserve. Since the Fed adopted this strategy, in conjunction with the Treasury department, their balance sheet has increased to more than USD $1.9 trillion.
The Federal Reserve has acquired all this not only by getting direct equity investments in banks and by easing standards on commercial paper purchases, but throughout efforts to remove asset backed securities from institutions.
More recently, the Fed has been considering buying assets, which will help them to add money to the financial system. It is important to take into account that Quantitative Easing put the US dollar to dangerous downside risks, just like what happened with the Yen. However, this strategy is the opportunity that the central bank has to consider, not only in order to stabilize the US economy, but also to avoid a deflationary spiral.
This article has been provided by www.forextradingbonus.com, website made by experts in financial and Forex markets that can help you to find the best Forex bonus for yourself.